Quick Start
This guide will help you get the basics of Edge Xpert up and running on your machine right away.
We will run Edge Xpert with its default services and utilize a service called the Virtual Device Service to simulate a flow of sensor data into the platform. In a real system this would be data from a real OT device based on Modbus, BACnet, OPC-UA, etc, but for a quick start demo the Virtual Device Service is ideal and does not require any external simulators.
We will use the Edge Xpert Manager UI to show how easy it is to administer the platform and verify that devices are connected and data is flowing.
Edge Xpert Installation
-
Install Edge Xpert
-
Verify that the prerequisites of Edge Xpert are installed as described here.
-
Download the latest Edge Xpert installer as described here.
-
To install the Edge Xpert Debian package run:
sudo dpkg -i edgexpert-<version_number>_amd64.deb -
Or, to install the Edge Xpert RPM package run:
sudo rpm -ivh edgexpert-<version_number>.x86_64.rpm -
Once installed, verify the installation by running the version command:
edgexpert -v
-
-
Install the Edge Xpert license file
-
Refer to Licensing for full instructions including how to access your commercial or evaluation license file.
-
To allow the Edge Xpert containers to access the license, ensure the license file is readable by the “other” user:
chmod +r <EdgeXpertLicenseFile>.lic -
Use the edgexpert license install command:
edgexpert license install <EdgeXpertLicenseFile>.lic -
You can verify the license was installed correctly:
Which will produce output similar to:edgexpert license checkEdge Xpert Licensing: Validating License File <EdgeXpertLicenseFile>.lic Edge Xpert Licensing: Signature valid Edge Xpert Licensing: License valid
-
Running Edge Xpert
As described in the Introduction, Edge Xpert is a microservices-based edge software platform. In this tutorial we are going to start the default services of Edge Xpert along with the optional Manager UI and the Virtual Device Service which will provide us some simple simulation data that we can observe being collected by the platform.
The Virtual Device Service simulates a number of devices, each randomly generating data of various types and within configurable parameters. For example, the Random-Integer-Device will generate random integers.
Start the Edge Xpert Core Services, the Edge Xpert Manager and the Virtual Device Service as follows:
edgexpert up xpert-manager device-virtual
The output should be similar to the following. Note that the first time this command runs, the container images for each service will need to be pulled, so this could take a little time:
Creating core-command ... done
Creating mqtt-broker ... done
Creating core-data ... done
Creating core-metadata ... done
Creating device-virtual ... done
Creating redis ... done
Creating xpert-manager ... done
Creating core-keeper ... done
Verify that the microservices are started as follows:
edgexpert status
NAMES STATUS CREATED PORTS
core-keeper Up 54 seconds 55 seconds ago 0.0.0.0:59890->59890/tcp, :::59890->59890/tcp
xpert-manager Up 54 seconds 55 seconds ago 0.0.0.0:9090->9090/tcp, :::9090->9090/tcp
core-data Up 55 seconds 56 seconds ago 0.0.0.0:59880->59880/tcp, :::59880->59880/tcp
redis Up 55 seconds 56 seconds ago 6379/tcp
device-virtual Up 54 seconds 56 seconds ago 0.0.0.0:59900->59900/tcp, :::59900->59900/tcp
core-metadata Up 54 seconds 56 seconds ago 0.0.0.0:59881->59881/tcp, :::59881->59881/tcp
core-command Up 54 seconds 56 seconds ago 0.0.0.0:59882->59882/tcp, :::59882->59882/tcp
mqtt-broker Up 55 seconds 56 seconds ago 0.0.0.0:1883->1883/tcp, :::1883->1883/tcp
Using the Edge Xpert Manager UI
On a web browser, access the Edge Xpert Manager UI at localhost:9090.
The default login for a first time user is admin with the default password of admin. This can of course be changed for a deployment situation.
The Edge Xpert Manager Dashboard will display as below and includes the 6 Virtual Devices started by the Virtual Device Service:
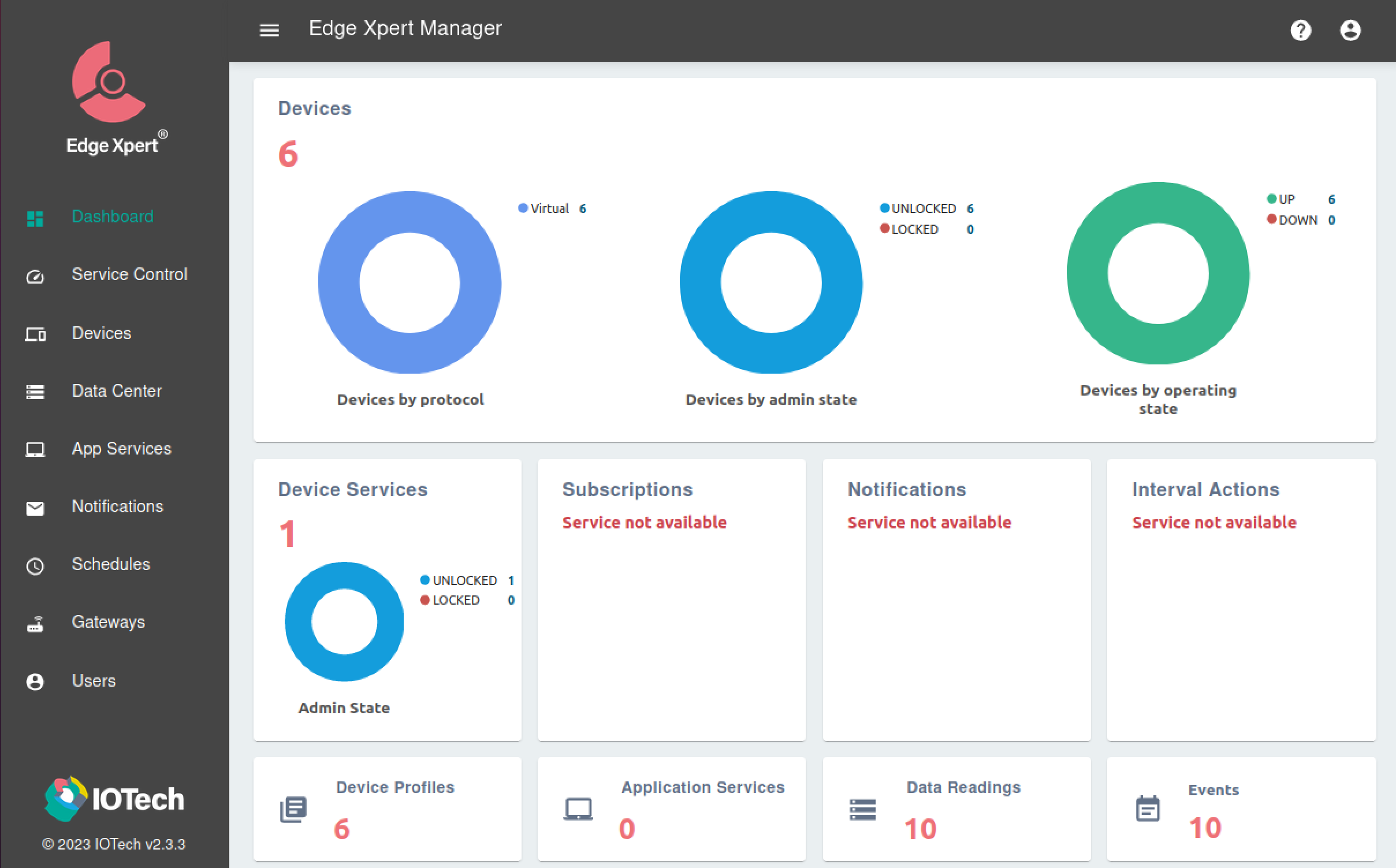
Clicking the Devices tab will show the 6 different Virtual Devices which should all be shown running correctly as Up and Unlocked.
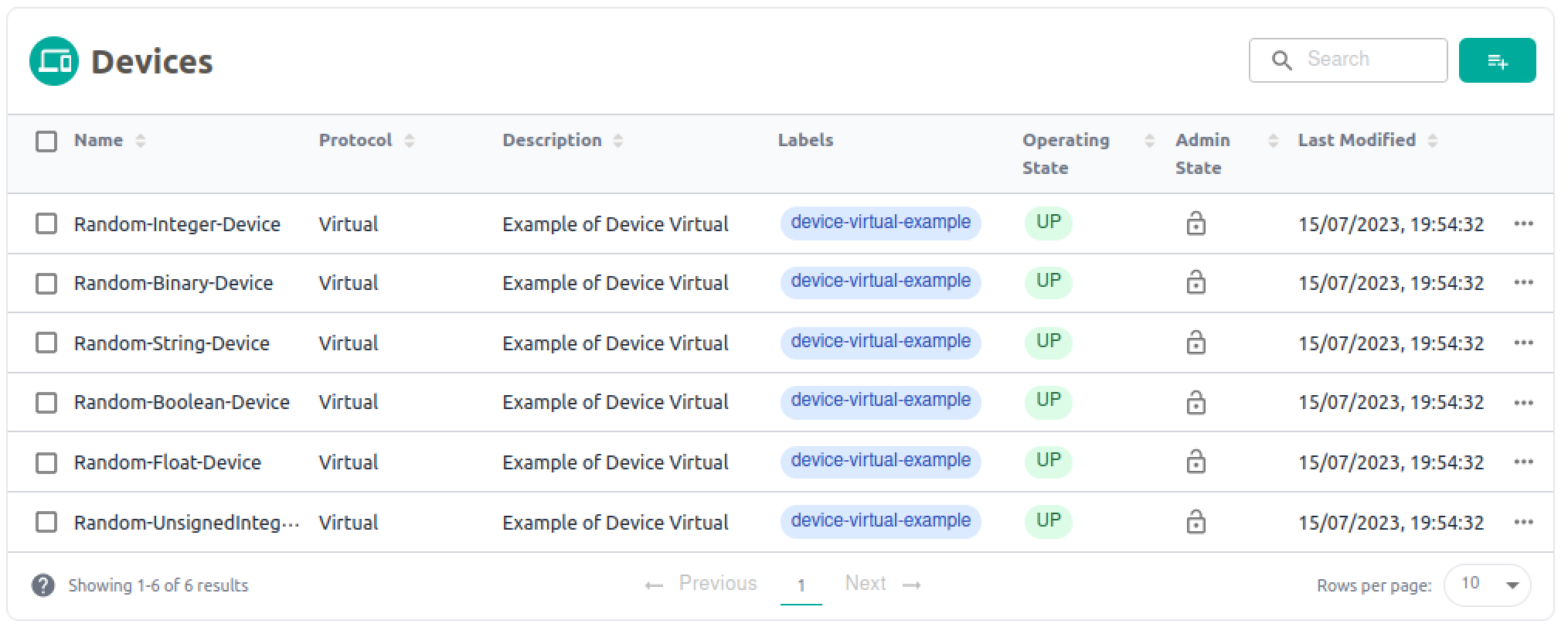
Refer to the Virtual Device Service section for more information of the different devices that are started and how they utilize Device Profiles.
By clicking the ACTIONS column at the end of the row, select the Control Device ![]() icon to read from or write data to one of the devices. You will see a list of commands with GET and SET operations.
icon to read from or write data to one of the devices. You will see a list of commands with GET and SET operations.
A call to GET of the Int16 device's Random-Integer-Device operation through Edge Xpert results in the next random value produced by the device in JSON format. You can execute one of these GET commands to return the values produced by the Int16 command, for example:
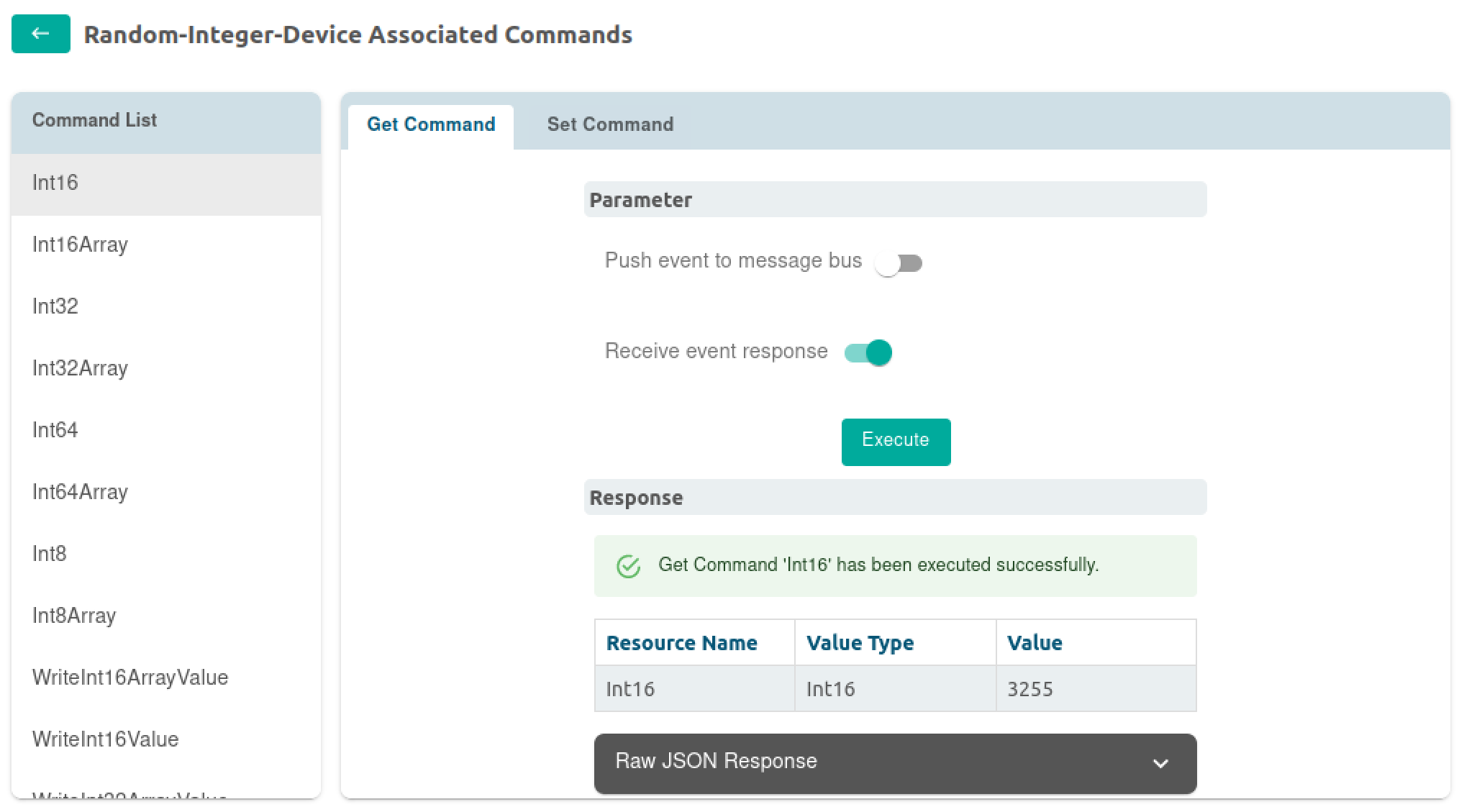
The default range for this reading is -32,768 to 32,767. In the example above, a value of 3255 was returned as the reading value.
With the service set up to randomly return values, the value returned will be different each time the Int16 GET command is sent. However, we can use the WriteInt16Value command to disable random values from being returned and instead specify a value to return. Using the UI, try executing a SET command with a specific value and then execute a GET again.
To view different data inputs over a period of time, select the Data Center tab. From there you can select data from specific devices and device resources and view these in table and graph form.
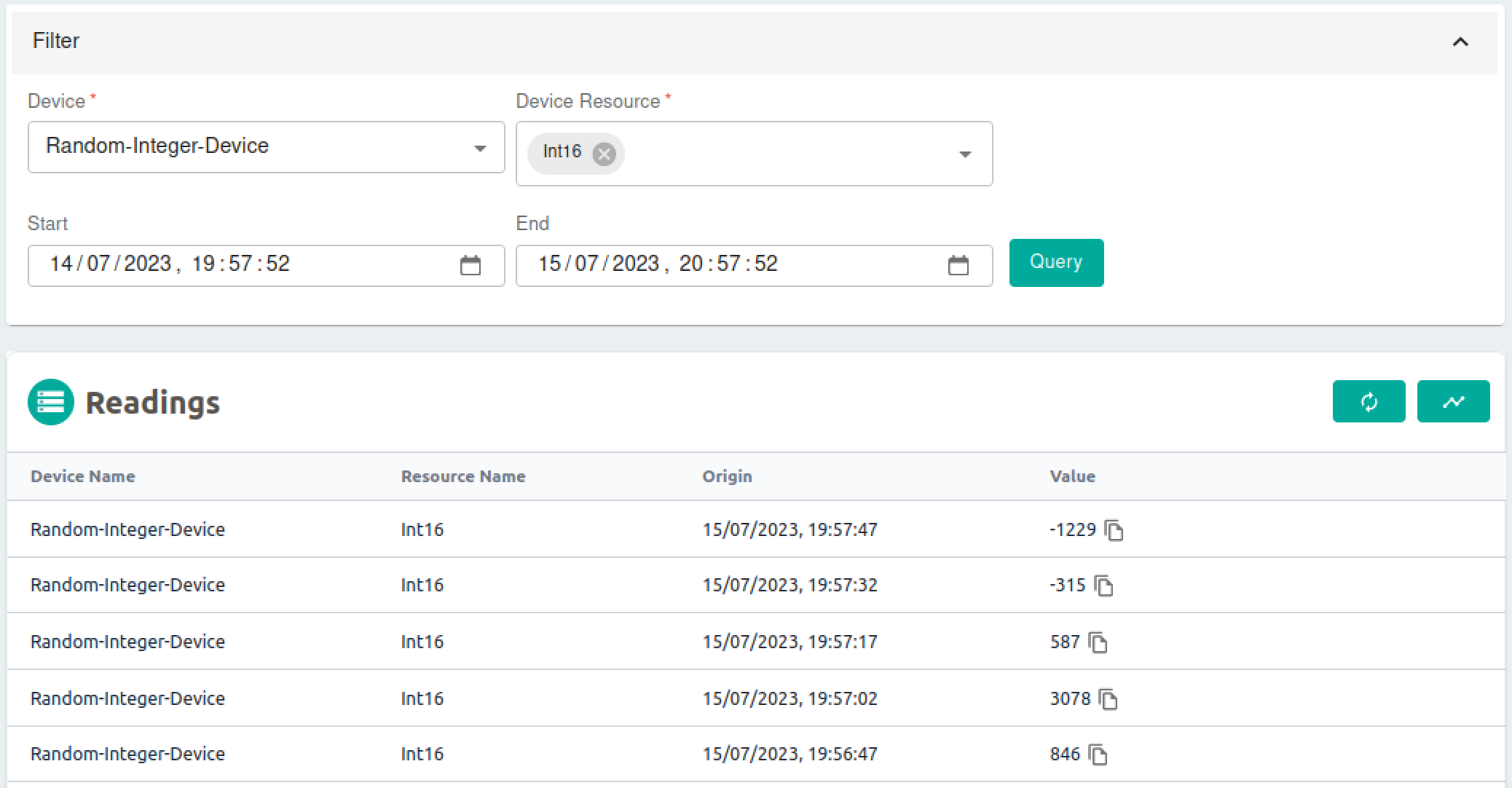
Note that you can see new data values for the Int16 device resource every 15 seconds. This is of course configurable, and set by the Auto Events associated with the device. You can see this information by clicking the View details ![]() icon for a particular device. You will learn more about device conifguration as you progress with Edge Xpert.
icon for a particular device. You will learn more about device conifguration as you progress with Edge Xpert.
Using the Edge Xpert APIs
The commands in Edge Xpert can be actioned via APIs as well as via the UI.
As a first example, the Edge Xpert API allows you to access data from a specific device with an API structure as follows:
http://localhost:59882/api/v2/device/name/Random-Integer-Device/Int16
This could be ran as a REST command in a web browser:
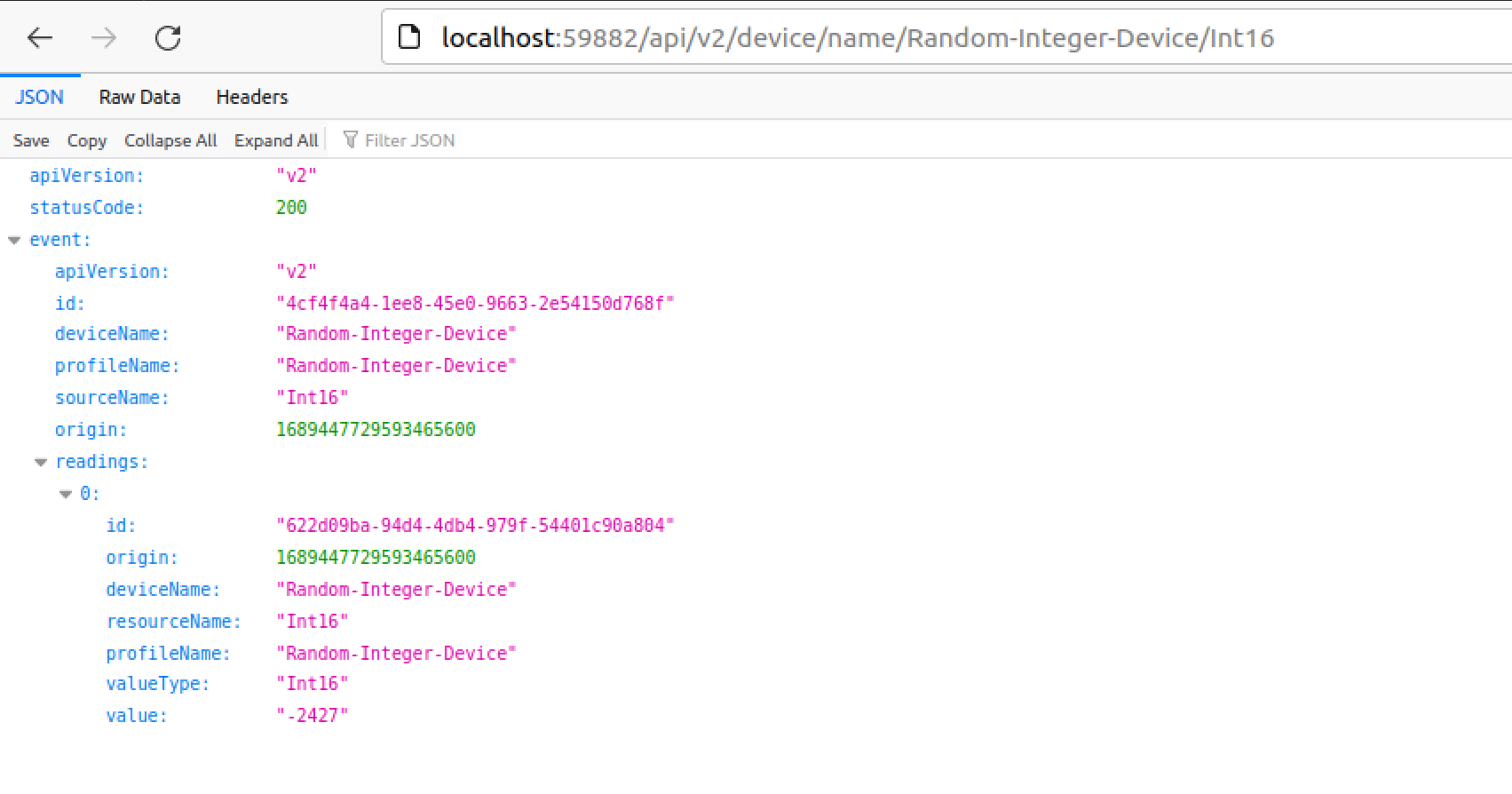
or via a comand line utility such as curl:
curl http://localhost:59882/api/v2/device/name/Random-Integer-Device/Int16 | jq
Info
jq is simply a JSON formatter
which would produce output as follows:
{
"apiVersion": "v2",
"statusCode": 200,
"event": {
"apiVersion": "v2",
"id": "8d9f4241-ca5f-49e8-b6ac-4b1fd32f9dcd",
"deviceName": "Random-Integer-Device",
"profileName": "Random-Integer-Device",
"sourceName": "Int16",
"origin": 1689628373043612000,
"readings": [
{
"id": "922022bf-fed4-4f9b-b336-aeafea758759",
"origin": 1689628373043612000,
"deviceName": "Random-Integer-Device",
"resourceName": "Int16",
"profileName": "Random-Integer-Device",
"valueType": "Int16",
"value": "5"
}
]
}
}
Edge Xpert provides a rich Programming API for device management, data access, rules, control, data sharing and so on. You will learn more about these as you progress with Edge Xpert.
Stopping Edge Xpert
As described here, the Edge Xpert CLI provides the stop, down, and clean commands that can all stop the Edge Xpert services.
Note
In addition to stopping the services, down deletes all Edge Xpert containers
In addition to stopping the services and deleting all containers, clean deletes any volumes or networks used by Edge Xpert
For example, to stop all running Edge Xpert services and delete the containers, use the down command, as shown below:
edgexpert down
The output from this command is similar to the following, depending on the services currently running:
Stopping xpert-manager ... done
Stopping core-keeper ... done
Stopping core-data ... done
Stopping mqtt-broker ... done
Stopping redis ... done
Stopping core-metadata ... done
Stopping device-virtual ... done
Stopping core-command ... done
Removing xpert-manager ... done
Removing core-keeper ... done
Removing core-data ... done
Removing mqtt-broker ... done
Removing redis ... done
Removing core-metadata ... done
Removing device-virtual ... done
Removing core-command ... done
Next Steps
Having completed this first tutorial it is recommended that users progress to the Chemical Tank Tutorial that demonstrates more key aspects of Edge Xpert including onboarding simulated devices using real OT protocols, ingesting that data and making it available for dashboards, rules, control and cloud streaming.