Overview
Scheduler Overview
The Scheduler microservice provides an internal clock, which can start operations among all services in Edge Xpert.
The Scheduler calls an Edge Xpert API URL using REST at a specified time, known as an interval, to trigger an operation, known as an interval action. For example, the scheduler microservice periodically calls the Core Data API to clean up old events that have been exported.
Scheduler uses a REST API. For further information on the support scheduler API, see Edge Xpert API
Note
In Edge Xpert v2, the REST API provided by the Scheduler has changed to use Data Transfer Objects (DTOs) for all responses and for all POST/PUT/PULL requests. All query APIs (GET) which return multiple objects, such as /all. provide offset and limit query parameters.
Default Interval Actions
The following interval actions are configured by default:
- Clean up Core Data events that have been persisted for an extended period. Such events are removed to prevent the edge node from running out of space. This is the
ScrubAgedoperation. The scheduler parameters determine how often and where to call in Core Data to invoke the clean up.
Note
The removal of stale records occurs on a configurable schedule. By default, the default action is invoked once a day at midnight.
Scheduler Persistance
The intervals and interval actions are persisted in the database. Persistence is accomplished by the Scheduler DB located in the current configured database.
Info
By default, Redis DB is used to persist all the scheduler service information including intervals and interval actions.
ISO 8601 Standard
The times and frequencies defined in the scheduler service's intervals are specified using the international date/time standard - ISO 8061. So, for example, the start of an interval would be represented in YYYYMMDD'T'HHmmss format. 20180101T000000 represents January 1, 2018 at midnight. Frequencies are represented with ISO 8601 durations.
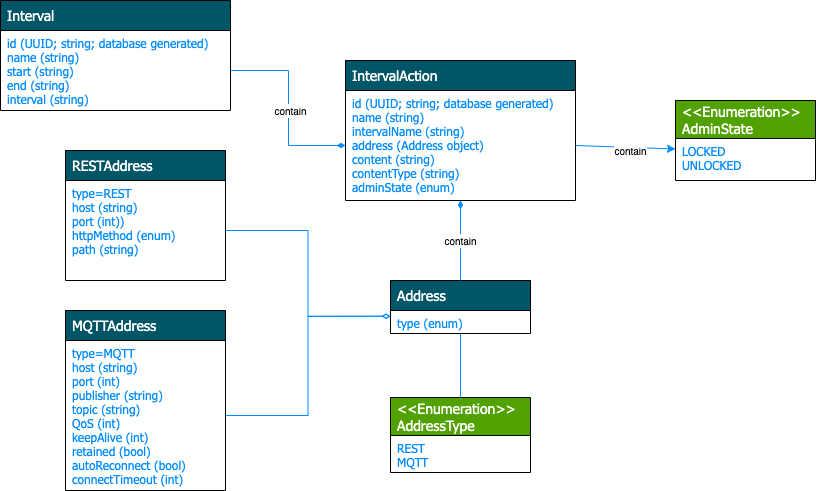
Scheduler Data Model
The following diagram shows the scheduler data model:
Note
Only RESTAddress is supported. The MQTTAddress may be implemented in a future release.
Data Dictionary
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| An object defining a specific "period" in time | |
| Id | Uniquely identifies an interval, for example a UUID |
| Created | A timestamp indicating when the interval was created in the database |
| Modified | A timestamp indicating when the interval was last modified |
| Name | the name of the given interval - unique for the EdgeX instance |
| Start | The start time of the given interval in ISO 8601 format |
| End | The end time of the given interval in ISO 8601 format |
| Interval | How often the specific resource needs to be polled. It represents as a duration string. The format of this field is to be an unsigned integer followed by a unit which may be "ns", "us" (or "µs"), "ms", "s", "m", "h" representing nanoseconds, microseconds, milliseconds, seconds, minutes or hours. Eg, "100ms", "24h" |
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| The action triggered by the service when the associated interval occurs | |
| Id | Uniquely identifies an interval action, for example a UUID |
| Created | A timestamp indicating when the interval action was created in the database |
| Modified | A timestamp indicating when the interval action was last modified |
| Name | the name of the interval action |
| Interval | associated interval that defines when the action occurs |
| AdminState | interval action state - either LOCKED or UNLOCKED |
| Content | The actual content to be sent as the body |
| ContentType | Indicates which request contentType should be used (i.e. text/html, application/json), the default is application/json |
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
An object inside IntervalActions indicating how to contact a specific endpoint by HTTP protocol |
|
| Type | Currently only support REST |
| Host | The host targeted by the action when it activates |
| Port | The port on the targeted host |
| HttpMethod | Indicates which Http verb should be used for the REST endpoint.(Only using when type is REST) |
| Path | The HTTP path at the targeted host for fulfillment of the action.(Only using when type is REST) |
See the REST API documentation for more information.
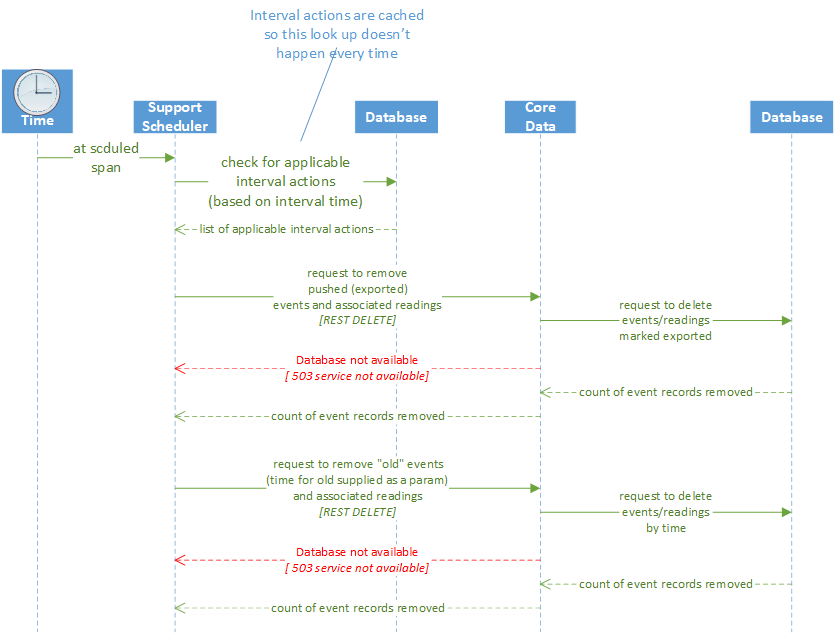
Scheduler High Level Interaction diagram
The following high-level interaction diagram shows the scheduler interval actions in cleaning up old and exported (pushed) records from Core Data:
Scheduler Configuration Properties
The following table shows the Scheduler configuration properties:
| Property | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ScheduleIntervalTime | 500 | the time, in milliseconds, to trigger any applicable interval actions |
| Property | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Default intervals for use with default interval actions | ||
| Name | midnight | Name of the every day at midnight interval |
| Start | 20180101T000000 | Indicates the start time for the midnight interval which is a midnight, Jan 1, 2018 which effectively sets the start time as of right now since this is in the past |
| Interval | 24h | defines a frequency of every 24 hours |
| Property | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration of the Core Data clean old events operation which is to kick off every midnight | ||
| Name | scrub-aged-events | name of the interval action |
| Host | localhost | run the request on Core Data assumed to be on the localhost |
| Port | 59880 | run the request against the default Core Data port |
| Protocol | http | Make a RESTful request to Core Data |
| Method | DELETE | Make a RESTful delete operation request to Core Data |
| Path | /api/v2/event/age/604800000000000 | request Core Data's remove old events API with parameter of 7 days |
| Interval | midnight | run the operation every midnight as specified by the configuration defined interval |