MQTT Management API
Edge Xrt provides an MQTT API with an associated set of messages and supporting topic hierarchy through which to manage both generic components and devices plus their data. This bi-directional API makes it easy to integrate Edge Xrt into third party platforms, applications or management systems, for example Edge Xpert.
The API supports the following groups of MQTT messages that can be used to manage Xrt components, devices and their data:
-
Component Management – messages provide List, Read, Update and Discovery operations for Components registered with Edge Xrt
-
Device Management – messages provide Create, Read, Update and Delete (CRUD) operations for Devices registered with Edge Xrt
-
Profile Management – messages provide CRUD operations for Device Profiles used to configure Xrt Device Services
-
Schedule Management – messages provide CRUD operations for Schedules used to control data polling rates associated with Device Resources
-
Device Discovery Management – messages provide operations that control the triggering of device auto discovery for protocols (e.g. BACNet, OPC UA, BLE) that provide such features
Note
Devices, profiles, and schedules have unique names scoped to a device service instance. This is also true for topics used to manage them. To understand how to configure a device service component and their topics please see: Device Service Component Configuration
All messages are encoded as JSON. Devices, Profiles, and Schedules have unique names scoped to a device service instance. All operations are in the form of an asynchronous Remote Procedure Call (RPC) over MQTT. The RPC is implemented a JSON request sent onto a request topic, with the JSON reply sent onto a reply topic. Unique request identifiers (usually a UUID) are used by the client to corrolate requests with replies. Note that internally all Xrt command and control work across the internal local bus (modelled on MQTT), however when bridged into MQTT, using the MQTT bridge component, it in effect acts as if part of an external MQTT hierarchy.
MQTT Topics
Each device service can be configured to support a number of MQTT topics used to support management via MQTT based RPC, these are:
| Configuration | Usage | Example | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|---|
| RequestTopic | Topic used to send operation requests to a device service | xrt/devices/bacnet/request | Yes |
| ReplyTopic | Topic used to send operation replies from a device service | xrt/devices/bacnet/reply | Yes |
| TelemetryTopic | Topic used to send generated telemetry (device readings) from a device service | xrt/devices/bacnet/telemetry | No |
| NotificationTopic | Topic used to send device status chage notifications from a device service | xrt/devices/notification | No |
| DiscoveryTopic | Topic used to send discovered device profiles from a device service | xrt/devices/bacnet/discovery | No |
The MQTT topics used to communicate are all configurable. An actual deployment would match the MQTT name space hierarchy
to correspond the actual set of deployed device services. Note that only request and reply topics are mandatory.
If topics for telemetry and discovery are not configured, this data is sent via the reply topic, where the type
field in the reply can be used to disambiguate message types. All MQTT RPC operations use the request and reply topics,
although typically the telemetry and discovery topics are used to separate the generated data stream from the reply
data. However the reply topic can be used, in which case a client needs to disambiguate reply data from generated telemetry and discovery.
If the notification topic is not configured, notifications are logged using the configured logger instead.
General Request Format
The RPC requests are represented as a JSON object with the following common fields:
| Key | Usage | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
| request_id | The unique request identifier. This can be any valid JSON and is used by a client to match a request with a reply. Typically this is a UUID string. | Yes |
| op | The operation name. Operation names are made up of two colon separated strings. The first identifies the target object and the second the operation
to be performed on this object. So the operation name to list devices is device:list. |
Yes |
| client | The client identity. This can be any valid JSON and is returned in the corresponding reply. | No |
| type | Message type string. Identifies message type and version. For a request this is currently "xrt.request:1.0".
If not set, it is assumed request is current supported version. |
No |
Additional operation-specific request fields may be required. These are described for each specific operation.
Example device:list Request:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "fa7cdd1a-c0ee-4578-b33b-444d777f2301",
"op": "device:list",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
General Reply Format
The RPC replies are represented as a JSON object with the following common fields:
| Key | Usage | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
| request_id | The unique request identifier. This is the request identifier sent in the corresponding request. | Yes |
| type | Message type string. Identifies message type and version. For a reply, this is currently "xrt.reply:1.0". |
Yes |
| result | Request result. Format depends on request type | Yes |
| client | The client identity. This is the client identifier sent in the corresponding request. | No |
General Result Format
Within each reply are results from the corresponding request. As a minimum a reply status is returned indicating a success or error category and an optional error message to provide more information.
| Key | Usage | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
| status | A numerical status. Zero indicating a success, other positive integers indicating a failure mode. | Yes |
| error | A string error, providing more information on failure. | No |
Additional operation-specific result fields may be present. These are described for each specific operation. The current set of supported status values is as follows:
| Value | Error Status | Enumeration |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Success | XRT_OPS_STATUS_OK |
| 1 | Not Found | XRT_OPS_STATUS_NOT_FOUND |
| 2 | Not Supported | XRT_OPS_STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED |
| 3 | Invalid Operation | XRT_OPS_STATUS_INVALID_OPERATION |
| 4 | Write Failed | XRT_OPS_STATUS_WRITE_FAILED |
| 5 | Read Failed | XRT_OPS_STATUS_READ_FAILED |
| 6 | Missing Data | XRT_OPS_STATUS_MISSING_DATA |
| 7 | Already Exists | XRT_OPS_STATUS_ALREADY_EXISTS |
| 8 | Store Failed | XRT_OPS_STATUS_STORE_FAILED |
| 9 | Load Failed | XRT_OPS_STATUS_LOAD_FAILED |
| 10 | Create Failed | XRT_OPS_STATUS_CREATE_FAILED |
| 11 | In Use | XRT_OPS_STATUS_IN_USE |
| 12 | Disabled | XRT_OPS_STATUS_DISABLED |
| 13 | Invalid Data | XRT_OPS_STATUS_INVALID_DATA |
| 14 | Update Failed | XRT_OPS_STATUS_UPDATE_FAILED |
| 15 | Timeout | XRT_OPS_STATUS_TIMEOUT |
Example Successful device:get Reply:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "94178bb8-a0ba-465f-ab31-77f1ba81537f",
"result":
{
"readings":
{
"BinaryInput1": { "origin": 1611161894180636200, "value": true, "type": "bool" }
},
"status": 0
},
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Example Failed Request Reply:
{
"client":"iotech",
"request_id":"101",
"result":
{
"error": "invalid operation",
"status": 3
},
"type":"xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Telemetry Format
Telemetry is data generated by a device service. This comes from either schedules created on a device or asynchronous events generated by a device. Telemetry data consists of a set of resources read from a device.
| Argument | Type | Configurable | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| device | string | No | The name of the device generating the telemetry |
| readings | object | No | Set of generated resource names and values |
| sourceName | string | Yes | If a scheduled reading, the name of the resource |
| type | string | No | Telemetry message type and version. For telemetry "xrt.telemetry:1.0" |
| tags | object | No | Telemetry tags. These can be configured on a device service, a schedule or a profile command |
Telemetry Tagging
User configurable tags can be added to generated telemetry. These can either be set at the scope of individual resources or at the scope of a telemetry message consisting of multiple resources.
| Tag Origin | Scope |
|---|---|
| Profile Resource | Resource |
| Profile Command | Message |
| Device Service Configuration | Message |
| Schedule Configuration | Message |
Configurable telemetry fields are not generated unless they have been specifically enabled via a device service configuration option.
Telemetry example:
{
"device":"SimpleServer",
"readings":
{
"analog_input_0:object-type": { "type":"uint32","value":0,"tags":{"Meta":true}},
"analog_input_0:present-value": { "type":"float32","value":1.55000000e+03 }
},
"tags":{"User":"Skye"},
"type":"xrt.telemetry:1.0"
}
Note
It is the user's responsibility to ensure that tags from different origins have unique key values.
Notification Format
Notifications are generated when the status of a device or device service changes, or if other administrative device events occur. The extent of events which may be reported varies from one device service to another, but may include such things as device connection / disconnection, controller state changes and diagnostic reports.
Notifications may additionally be generated by configuring a Bus Logger for any XRT component. This will generate notifications for every log message.
| Argument | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| component | string | Yes | The name of the component (typically a device service) generating the notification |
| timestamp | integer | Yes | The time at which the notification was generated |
| device_name | string | No | The name of the device to which the notification relates |
| severity | string | Yes | The importance of this notification. This is equivalent to a Log Level, ie ERROR, WARN, Info, Debug or Trace |
| event | string | Yes | Short name for the event that has occurred. This will generally use a vernacular appropriate to the device class in question, eg PNIO_ALARM_DEV_RETURN for Profinet devices connecting |
| message | string | Yes | A description of the event |
| details | object | No | Any other information |
XRT defines the following generic event names:
* XRT_LOG - identifies notifications from the Bus Logger component
* XRT_OPSTATE - the operational state of a device has changed. Here the details object will indicate the new state, eg {"state": "up"}
Notification example:
{
"component": "profinet",
"timestamp": 1663341779217648,
"device_name": "netHAT",
"severity": "Debug",
"event": "PNIO_CBE_DEV_ACT_CONF",
"message": "Device has been activated",
"details":
{
"result": 0
}
}
Device Format
Devices represent a physical device connected to an Xrt device service. Device data can be generated via discovery, or manually specified.
| Argument | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | Yes | The name of the device |
| profileName | string | Sometimes | The name of the profile associated with the device |
| protocols | object | Yes | Set of protocols associated with the device |
| properties | object | No | Set of properties associated with the device |
| scheduleDeadBand | integer | No | Deadband for schedules run on the device (in milliseconds) |
Device example:
{
"name": "3befe158-ed46-4afc-b838-7bcf96b4e414",
"profileName": "modbus-sim",
"protocols":
{
"modbus-rtu":
{
"Address": "/tmp/virtualport",
"BaudRate": 19200,
"DataBits": 8,
"Parity": "N",
"StopBits": 1,
"UnitID": 3
}
},
"properties":
{
"vendor": "IOTech"
},
"scheduleDeadBand": 1000
}
Note
The device name may be used as the device object key, so it may not be explicitly set in the JSON object representation, for example in device discovery format.
Schedule Format
Schedules are used to register timed, polled reads of device resources, or add asynchronous notification support. Note that asynchronous notification support is protocol specific. If a protocol specific asynchronous notification is configured and a device service is unable to support this (for example due to resource limit constraints) then, if an interval is also set, a schedule will be created instead.
| Argument | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | Yes | The name of the schedule. |
| device | string | Yes | The name of the device on which the schedule is run. |
| resource | string or array of strings | Yes | The resource name or array of resource names to be read. Names can be regular expressions. |
| interval | integer | No | Interval at which schedule is to run in microseconds. Optional if asynchronous notification also configured. |
| on_change | boolean | No | Whether only changed values are published. Default value is false. |
| tags | object | No | Tags added to generated telemetry messages. |
| units | boolean | No | Whether to publish resource units for polled reads if specified in a profile. Default value is false. |
| options | object | No | Protocol specific options. |
Note that resource names can also be regular expressions, so for example to schedule a read on all digital inputs
"Digital Input*" could be used.
Schedule example with BACnet COV registration and fallback polling:
{
"name": "1c28183b-837f-466d-84c5-42a6bcfcf428",
"device": "15d6b69e-2d9a-48a3-a433-cb6e42929804",
"resource": ["Universal Input 2:present-value","Universal Input 2:units"],
"interval": 5000000,
"tags": {"Group":"Input2"},
"options": { "COV": { "Confirmed": true, "Lifetime": 360 } }
}
Device Discovery Format
Discovery data is generated by a device service for a protocol that supports device discovery. Discovery semantics are controled by the set
of supported discovery operations. By default discovery data is generated on the discovery topic. Discovery can be configured to occur on
a scheduled interval or explicity invoked with the discovery:trigger operation.
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| devices | object | Set of meta-data for discovered devices. With each device name used as a key for the device meta information. |
| type | string | Discovery message type and version. For discovery "xrt.device.discovery:1.0" |
Discovery example:
{
"type": "xrt.device.discovery:1.0",
"devices":
{
"SimpleServer":
{
"properties":
{
"ApplicationSoftware": "1.0",
"Contactable": true,
"DeviceType": "BACnet-IP",
"Firmware": "1.0.0",
"IP": "192.168.4.18",
"InstanceID": 2345,
"ModelName": "IOTech SIM",
"ObjectName": "SimpleServer",
"Port": 47808,
"VendorID": 1313,
"VendorName": "IOTech"
},
"protocols": { "BACnet-IP": { "DeviceInstance": 2345 } }
}
}
}
Reading Format
A reading represents a resource (value) on a device that can be read or written. Reading can be generated via an explicit device get operation, a repeating scheduled reading or an asynchronous device notification. Readings can be written via device put operations.
| Argument | Type | Description | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | string | A string representing the data type of the value | Yes |
| value | varying | The data value | Yes |
| origin | integer | The data timestamp in nanoseconds | No |
| tags | object | Tags associated with the resource in a profile | No |
| units | string | Units associated with the resource in a profile | No |
Multiple readings are represented as a JSON object where the associated resource name string is a key for the associated reading. Readings that have been read can have an optional timestamp (enabled via configuration of a device service).
Readings example:
{
"BinaryInput1": { "origin": 1611161894180636200, "type": "bool", "value": true },
"AnalogInput1": { "origin": 1611161894180636220, "type": "uint32", "value": 3423 },
"Status": { "origin": 1611161894180636240, "type": "stringarray", "value": [ "disabled", "active" ] }
},
The following set of reading data types are supported:
| Name | Type | JSON Example |
|---|---|---|
| bool | Boolean | true |
| int8 | Signed 8 bit integer | -12 |
| uint8 | Unsigned 8 bit integer | 123 |
| int16 | Signed 16 bit integer | -1234 |
| uint16 | Unsigned 16 bit integer | 1234 |
| int32 | Signed 32 bit integer | -1234567 |
| uint32 | Unsigned 32 bit integer | 1234567> |
| int64 | Signed 64 bit integer | -1234567890123 |
| uint64 | Unsigned 64 bit integer | 1234567890123 |
| boolarray | Array of boolean | [true, false, true]> |
| int8array | Array of signed 8 bit integers | [-128, 0, 127] |
| uint8array | Array of unsigned 8 bit integers | [0, 1, 2] |
| int16array | Array of signed 16 bit integers | [-32768, 0, 32767] |
| uint16array | Array of unsigned 16 bit integers | [0, 1, 2, 65535] |
| int32array | Array of signed 32 bit integers | [-2147483648, 0, 2147483647] |
| uint32array | Array of unsigned 32 bit integers | [0, 1, 2, 4294967295] |
| int64array | Array of signed 64 bit integers | [-9223372036854775808, 0, 9223372036854775807] |
| uint64array | Array of unsigned 64 bit integers | [0, 1, 2, 18446744073709551615] |
| string | A String | "an example string" |
| stringarray | Array of strings | ["string1", "string2", "string3"] |
| binary | A base64 encoded binary string | "ASNFZw==" |
| object | Composed object type | {"value" : { "example" : 1234}} |
| objectarray | Array of composed objects | [{"value1" : 1234}, {"value2" : 5678}] |
Note that array types can support multi-dimensional arrays:
Multi-dimensional integer array JSON example:
[[1,2,3], [4,5,6]]
Component Management
Component management operations are supported on an Xrt server instance containing a command component. See Command Component
The component management functions are essentially to support the dynamic discovery and update of component configurations. Dynamic re-configuration is only supported on a per component basis, see component specific documentation to determine what features are supported. Operations are supported to list, read, update and discover components.
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| "component:list" | List components |
| "component:read" | Read a component state and configuration information |
| "component:update" | Update a component configuration information |
| "component:discover" | Discover state and configuration of all components |
| "component:exit" | Causes all components to exit and server process to terminate |
List Components
Return a list of component names.
Operation: component:list
Request example:
{
"client": "client0",
"request_id": "0eb23c34-b38a-4e46-96ac-d1fb2b8c5597",
"op": "component:list",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Reply example:
{
"client": "client0",
"request_id": "0eb23c34-b38a-4e46-96ac-d1fb2b8c5597",
"result":
{
"components": ["bus","logger","pool","sched","bacnet","mqtt_bridge"],
"status": 0
},
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Read Component
Returns the state of a named component.
Operation: component:read
Request example:
{
"client": "client0",
"request_id": "462cd4fe-caf7-4f2b-83b3-f32084866087",
"op": "component:read",
"component": "logger",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Reply example:
{
"client": "client0",
"request_id": "462cd4fe-caf7-4f2b-83b3-f32084866087",
"result":
{
"component":
{
"name":"logger",
"state":"Running",
"type":"IOT::Logger",
"category": "IOT::Core",
"config":{"Level":"Debug","Name":"console"}
},
"status": 0
},
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Update Component
Updates the state of a named component. Currently only the component configuration can be updated.
Operation: component:update
Request example:
{
"client": "client0",
"request_id": "33aab1e3-44d0-4e01-9487-fe9e9cd51a9e",
"op": "component:update",
"component": "logger",
"config": { "Level": "info" }
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Reply example:
{
"client": "client0",
"request_id": "33aab1e3-44d0-4e01-9487-fe9e9cd51a9e",
"result": { "status": 0 },
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Discover Components
Discover set of installed components. State and configuration for each component is published. The optional category parameter can be used to filter on the category of components returned.
Operation: component:discover
Request example:
{
"client": "client2",
"request_id": "929950d5-2323-4b6f-a102-9ee423c2ecac",
"op": "component:discover",
"category": "IOT::Core",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Reply example:
{
"client": "client2",
"request_id": "929950d5-2323-4b6f-a102-9ee423c2ecac",
"result":
{
"status": 0,
"components":
[
{
"name": "xrt",
"state": "Running",
"type": "XRT::Config",
"category": "IOT::Core",
"config": { "NodeId": "azathoth", "ServerId": "bacnet-ip-server" }
},
{
"name": "logger",
"state": "Running",
"type": "IOT::Logger"
"category": "IOT::Core",
"config": { "Level": "Debug", "Name": "console" },
}
]
},
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Exit Components
Exit all components and terminate server process. When Xrt is deployed using systemd, this causes a restart of the Xrt server instance. This supports applying new component configurations that cannot be updated dynamically. The server ID in the request must match the server ID of the Xrt instance, or the wild card "*" is used. This supports shutting down multiple Xrt instances via a shared command Topic. A delay (in milliseconds) can also be set before the server process exits (this defaults to one second). If a server delay is set at zero or a small period (less than a hundred or so milliseconds), the server may exit before the command reply can be sent.
Operation: component:exit
Request example:
{
"client": "manager",
"request_id": "963b8fd1-4bd5-42cb-b10f-adf20ff0b461",
"op": "component:exit",
"server_id": "*",
"delay": 5000,
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Reply example:
{
"client": "manager",
"request_id": "963b8fd1-4bd5-42cb-b10f-adf20ff0b461",
"result": { "status": 0 },
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Device Management
Device management operations are supported on all device service components of an Xrt server instance.
Operations are supported to list, add, delete, read and update devices. In addition put and get operations support reading and writing device resources (data points). Note that discovered devices have an auto-generated UUID string for a name, manually configured devices can use more meaningful names.
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| "device:add" | Add a new device |
| "device:delete" | Delete an existing device |
| "device:list" | List devices |
| "device:read" | Read a device meta information |
| "device:update" | Update a device meta information |
| "device:scan" | Scan a device to generate a profile |
| "device:put" | Write one or more values to a device |
| "device:get" | Read one or more values from a device |
The core management options are intended to be generic and portable across multiple protocols, although not all features
are supported on all protocols (such as device discovery). However protocol-specific data can be required for the
management of advanced or non standard features. This is handled via optional options fields in a variety of operations, details
of these additional options are covered in the protocol specific documentation.
Device telemetry is controlled by schedules below.
List Devices
Return a list of device names.
Operation: device:list
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "fa7cdd1a-c0ee-4578-b33b-444d777f2301",
"op": "device:list",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Reply example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "fa7cdd1a-c0ee-4578-b33b-444d777f2301",
"result":
{
"devices":
[
"a18342fe-5c53-451e-829e-2b7063397caf", "c73cee57-05cd-4fac-9d8b-987026831927",
"4bf7d20f-5a4d-42ab-a939-bfbabdf17500", "855458fd-9cdd-4022-97d3-d1b79d3653bd",
"892db3be-73ff-43fb-9525-ca84a919952c", "cc9a85ee-e944-4430-9eeb-b29beea29301"
],
"status": 0
},
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Add a Device
Adds a named device with meta information. If no profile name is specified
the device will be created but will not be usable until the profile is set,
for example by a device:update operation.
Operation: device:add
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | Request | Name of device to add |
| device_info | object | Request | Device meta-data |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "404be6e3-e171-4547-bacb-151dfe0ae483",
"op": "device:add",
"device": "3befe158-ed46-4afc-b838-7bcf96b4e414",
"device_info":
{
"profileName": "opc-ua-sim-profile",
"protocols": { "OPC-UA":{ "Address": "localhost:49947", "Security": "None" } }
},
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "404be6e3-e171-4547-bacb-151dfe0ae483",
"result": { "status": 0 },
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Scan a Device
This operation checks a device profile for updates. If no profile name is provided and the discovered profile is different from the existing profile, then a new UUID profile is generated, otherwise the existing profile remains unchanged. If a profile name is provided, a new named profile is always created even if the discovered profile is the same as the existing profile.
Operation: device:scan
| Argument | Type | Context | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| device | string | Request | Yes | Name of device to scan |
| profile | string | Request | No | Name of the profile to generate. Must not already exist. |
| options | object | Request | No |
Xrt and device service specific scan options
The following Xrt options are available: DiscoverInitialValues - Boolean controlling whether to include initially discovered values in the generated profile.
This will override what was set in the device service configuration
|
| profile | string | Result | N/A | Name of profile associated with device |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "f07be237-8928-429c-b236-6fa1c59da216",
"op": "device:scan",
"device": "f02f87c9-6248-45e6-ac0f-1d74e20049ba",
"profile": "NewProfile",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "f07be237-8928-429c-b236-6fa1c59da216",
"op": "device:scan",
"device": "bacnet-ip-sim1",
"options": { "DiscoverInitialValues": false, "DiscoverProperties": [75, 36, 28, 81, 85, 103, 117, 87], "DiscoverObjects": [8, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 13, 14, 19] },
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Reply example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "f07be237-8928-429c-b236-6fa1c59da216",
"result":
{
"profile": "a3269a76-fc83-44ac-b3ca-2ecb7a7c4965",
"status": 0
},
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Read Device Information
Returns meta-data information on a named device.
Operation: device:read
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| device | string | Request | Name of device to read |
| device | object | Result | Device meta-data |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "73450fca-abdc-44af-be7d-65ca9fe3ffc1",
"op": "device:read",
"device": "3befe158-ed46-4afc-b838-7bcf96b4e414",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "73450fca-abdc-44af-be7d-65ca9fe3ffc1",
"result":
{
"device":
{
"name": "3befe158-ed46-4afc-b838-7bcf96b4e414",
"profileName": "AI 4xU/I 2-wire ST_1",
"protocols": { "Profinet": { "I-base": "0", "Q-base": "0" } },
"properties":
{
"name" : "AI 4xU/I 2-wire ST",
"description" : "Analog input module AI4 x U/I 2-wire ST; 16-bit, common mode voltage 10 V; configurable diagnostics; supports PROFIenergy",
"vendor": "SIEMENS"
}
},
"status": 0
},
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Update Device Information
Change meta-data on a named device.
Operation: device:update
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| device | string | Request | Name of device to update |
| device_info | object | Request | Meta-data update for device |
The device_info fields that can be updated in the request are:
- profileName (string)
- protocols (object)
- properties (object)
- operational (boolean)
- enabled (boolean)
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "815cf17b-1c19-4d66-b0fa-ff217dbca97e",
"op": "device:update",
"device": "3befe158-ed46-4afc-b838-7bcf96b4e414",
"device_info": { "profileName": "AI 4xU/I 2-wire ST_2" },
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "815cf17b-1c19-4d66-b0fa-ff217dbca97e",
"result": { "status": 0 },
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Delete a Device
Deletes a named device.
Operation: device:delete
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| device | string | Request | Name of device to be deleted |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "ae813a79-c11c-459b-bf27-874699774025",
"op": "device:delete",
"device": "bacnet-ip-sim1",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Get Device Resources
Read one or more resource values from a device.
Operation: device:get
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| device | string | Request | Name of device from which to read resources |
| resource | string or array of strings | Request | Resource name or array of resource names, or regular expressions, to be read from the device |
| readings | object | Result | Set of resource readings |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "94178bb8-a0ba-465f-ab31-77f1ba81537f",
"op": "device:get",
"device": "damocles-0002b503c1ec",
"resource": "BinaryInput1:present-value",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "94178bb8-a0ba-465f-ab31-77f1ba81537f",
"result":
{
"readings":
{
"BinaryInput1": { "origin": 1611161894180636200, "value": true, "type": "bool" }
},
"status": 0
},
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Put Device Resources
Write one or more resource values to a device
Operation: device:put
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| device | string | Request | Name of device on which to write resources |
| values | object | Request | Set of resource names and values to write to device |
| options | object | Request | Protocol specific write options |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "37d6faf3-8e0b-4f52-b02c-cdd833cbb528",
"op": "device:put",
"device": "damocles-0002b503c1ec",
"values":
{
"BinaryOutput2:present-value": false,
"BinaryOutput1:present-value": true
},
"options": { "Priority":5 },
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Profile Management
Operations are supported to list, add, delete, read and update profiles. A profile provides meta-data about all resources (values) that can be read or written to a device and allows these resources to be referenced by name in commands that access them. Profiles can be hand written (not recommended), generated via the IOTech web-based Device Configuration Tool (DCT) or discovered from a device (recommended), when supported by the protocol. As many real industrial devices may support many thousands of resources, manual generation of profiles is not feasible so discovery should be used wherever possible. Discovered profiles have a UUID string as a name.
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| "profile:add" | Add a new profile |
| "profile:delete" | Delete an existing profile |
| "profile:list" | List profiles |
| "profile:read" | Read a profile |
| "profile:update" | Update a profile |
List Profiles
Return a list of profile names.
Operation: profile:list
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| profiles | string array | Result | Set of known profile names |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "4fe9d670-eba7-474a-9f2a-8f22b695d32a",
"op": "profile:list",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "4fe9d670-eba7-474a-9f2a-8f22b695d32a",
"result":
{
"profiles":
[
"fe04cd4b-1330-460e-bae9-eb75c8c0d556", "dd609c4d-a170-4289-a7f1-4ea0957423a3",
"9ef618cc-2cce-4305-a577-3548344456a2", "912692af-8fcc-4174-812c-06db9617dfda"
],
"status": 0
},
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Add a Profile
Adds a profile.
Operation: profile:add
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| profile | object | Request | Profile to add |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "66961ca5-d962-44d6-92d9-3f6c76ffc63a",
"op": "profile:add",
"profile":
{
"description": "Settings for Originator to Target Implicit Data Exchange",
"labels": [],
"deviceResources":
[
{
"name": "Implicit O2T Settings",
"attributes": { "type": "O2TSettings", "assemblyID": 112, "size": 496, "includeHeader32bit": true },
"properties": { "valueType": "String", "readWrite": "R" }
}
],
"name": "6c52903d-e942-4275-8f48-e8d927f3d2a6",
"model": "DI 8x24VDC ST V1.0"
},
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Read Profile Information
Returns information on a named profile.
Operation: profile:read
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| profile | string | Request | Name of profile to read |
| profile | object | Result | Read profile |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "ae87de5c-3dd8-45c6-9101-2e0f7a92e402",
"op": "profile:read",
"profile": "6c52903d-e942-4275-8f48-e8d927f3d2a6",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "ae87de5c-3dd8-45c6-9101-2e0f7a92e402",
"result":
{
"profile":
{
"description": "Digital input module DI8 x 24VDC ST; configurable diagnostics; input delay 0 to 20ms; input type 3 (IEC 61131); supports PROFIenergy",
"labels": [],
"deviceResources":
[
{
"description": "Inputs",
"properties": { "valueType": "uint8", "readWrite": "R" },
"name": "Inputs",
"attributes": { "I-offset": "0" }
}
],
"name": "6c52903d-e942-4275-8f48-e8d927f3d2a6",
"model": "DI 8x24VDC ST V1.0"
},
"status": 0
},
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Update a Profile
Replaces a named profile.
Operation: profile:update
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| profile | object | Request | Updated profile |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "7502b4e0-178d-4adc-961a-a312d28f1b0c",
"op": "profile:update",
"profile":
{
"name": "bacnet-ip-sim-profile",
"description": "Profile for IOTech BACnet Simulator",
"model": "IOTech BACnet Simulator",
"labels": [],
"deviceResources":
[
{
"attributes": { "instance": 1, "property": 85, "type": 1 },
"name": "analog_output_1:present-value",
"properties": { "readWrite": "RW", "valueType": "float32" }
}
]
},
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Delete a Profile
Removes a named profile.
Operation: profile:delete
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| profile | string | Request | Name of profile to delete |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "bddf5eba-db8c-442b-bd68-c7b505e8095c",
"op": "profile:delete",
"profile": "6c52903d-e942-4275-8f48-e8d927f3d2a6",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Schedule Management
Operations are supported to list, add, delete, read and update schedules. Schedules are used to regularly poll a device for resources. Also protocol specific extensions are supported to register asynchronous device generation of data (typically when an input value changes) or other events.
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| "schedule:add" | Add a new schedule |
| "schedule:delete" | Delete an existing schedule |
| "schedule:list" | List schedules |
| "schedule:read" | Read a schedule |
| "schedule:update" | Update a schedule |
List Schedules
Return a list of schedule names.
Operation: schedule:list
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| schedules | string array | Result | Array of schedule names |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "1e92b97e-47b0-4cc0-a4d1-5f927c2d87d9",
"op": "schedule:list",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "1e92b97e-47b0-4cc0-a4d1-5f927c2d87d9",
"result":
{
"schedules":
[
"5d9e8fbd-6e02-49fa-9d87-7ecfefc6f564",
"b7883904-fe0c-4352-9e93-9c4225dc3daa",
"eedd0583-af3c-4d32-9fc1-f1a6fa157daa"
],
"status": 0
},
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Add a Schedule
Adds a schedule.
Operation: schedule:add
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| schedule | object | Request | Schedule to add |
Request example including BACnet COV registration:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "a5755ee5-d937-4043-ba2b-39ac6bef3418",
"op": "schedule:add",
"schedule":
{
"name": "1c28183b-837f-466d-84c5-42a6bcfcf428",
"device": "15d6b69e-2d9a-48a3-a433-cb6e42929804",
"resource": ["Universal Input 2:present-value","Universal Input 2:units"],
"interval": 5000000,
"options": { "COV": { "Confirmed": true, "Lifetime": 360 } }
},
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Read Schedule Information
Returns information on a named schedule.
Operation: schedule:read
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| schedule | string | Request | Name of schedule to read |
| schedule | object | Result | Read schedule |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "a5755ee5-d937-4043-ba2b-39ac6bef3418",
"op": "schedule:read",
"schedule": "a5755ee5-d937-4043-ba2b-39ac6bef3418",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "a5755ee5-d937-4043-ba2b-39ac6bef3418",
"result":
{
"schedule":
{
"id": "a5755ee5-d937-4043-ba2b-39ac6bef3418",
"device": "15d6b69e-2d9a-48a3-a433-cb6e42929804",
"resource": [ "BinaryInput1:present-value", "BinaryInput2:present-value" ],
"interval": 5000000
},
"status": 0
},
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Update a Schedule
Replaces a named schedule.
Operation: schedule:update
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| schedule | object | Request | Schedule to update |
Request example:
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "99baccaf-2fbc-4377-80da-56bc16555cb9",
"op": "schedule:update",
"schedule":
{
"name": "1c28183b-837f-466d-84c5-42a6bcfcf428",
"device": "15d6b69e-2d9a-48a3-a433-cb6e42929804",
"resource": "BinaryInput1:present-value",
"interval": 5000000,
"on_change": true,
},
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Delete a Schedule
Removes a named schedule.
Operation: schedule:delete
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| schedule | string | Request | Name of schedule to delete |
Request arguments: schedule name
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "f7ad39e4-5b39-4293-b4ba-723c46872469",
"op": "schedule:delete",
"schedule": "1c28183b-837f-466d-84c5-42a6bcfcf428",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Device Discovery Management
Operations are supported to read and update device discovery options and explicitly trigger discovery.
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| "discovery:read" | Read device discovery options |
| "discovery:update" | Update device discovery option |
| "discovery:trigger" | Trigger device discovery |
Read Discovery Options
Returns the current discovery and re-discovery modes and scheduled interval.
Operation: discovery:read
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| mode | string enumeration | Result | Discovery mode, "enabled", "disabled" or "unavailable" if cannot be determined from device |
| interval | integer | Result | Discovery poll interval in seconds |
Request example:
{
"client":"client1",
"request_id": "abb2fa4f-68b8-4129-9df9-801c63e1d05f",
"op": "discovery:read",
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
{
"client": "client1",
"request_id": "abb2fa4f-68b8-4129-9df9-801c63e1d05f",
"result":
{
"mode": "enabled",
"interval": 0,
"status": 0
},
"type": "xrt.reply:1.0"
}
Update Discovery Options
Changes discovery mode and scheduled interval.
Operation: discovery:update
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| enable | boolean | Request | Whether to enable or disable discovery |
| interval | integer | Request | Discovery poll interval in seconds |
Request example:
{
"client":"client1",
"request_id": "b2d4710e-a6dc-4102-a9f7-e67cdfbb9c27",
"op": "discovery:update",
"enable": true,
"interval": 3600,
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
Trigger Discovery
Triggers an immediate device discovery. Discovered devices are published to the discovery topic. Having discovery disabled does not effect this operation as the enable option is only applied to scheduled discovery.
Operation: discovery:trigger
| Argument | Type | Context | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| options | object | Request | Protocol specific discovery trigger options |
Request example:
{
"client":"client1",
"request_id": "a40c10f6-8489-401a-ac5f-5bd9942e995c",
"op": "discovery:trigger",
"options":
{
"DiscoveryDuration": 5000,
"DiscoveryRetries": 2,
"DiscoveryDeviceRange": [0, 999]
},
"type": "xrt.request:1.0"
}
API Usage Patterns
There are multiple usage patterns that can be achieved using the Xrt message API.
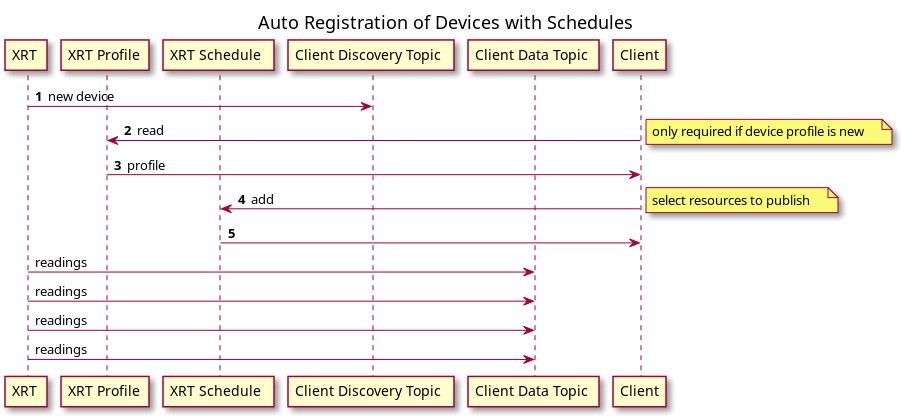
Auto Registered Devices
Auto registration of new discovered devices can be enabled by setting the “AutoRegister” configuration property to true. The following sequence diagram show the sequence of messages exchanged to publish data from a newly discovered device.
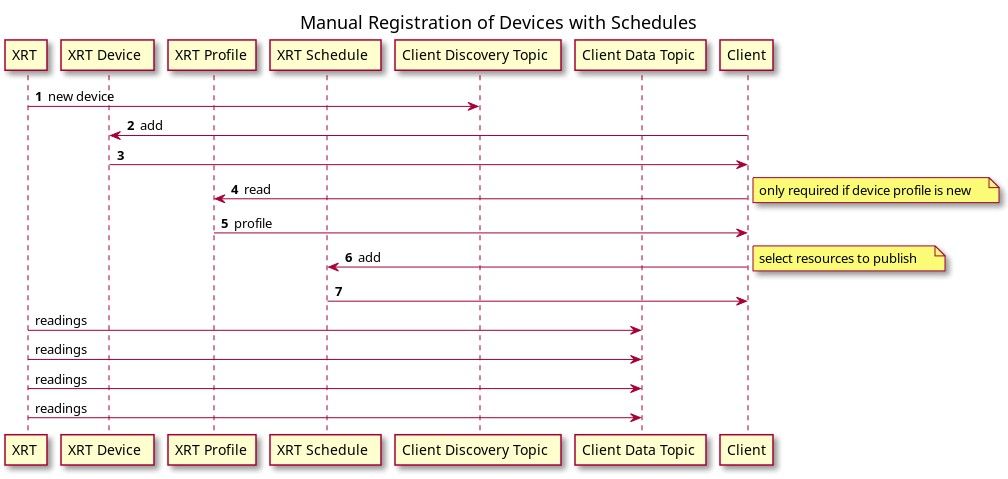
Manual Device Registration